Cloud security needs to be continuously improved and refined. “It’s a critical part of your overall organizational security,” insists Rob Lee, Chief Curriculum Director for SANS Amazon.
AWS is an easy-to-use, scalable and flexible cloud computing solution. It was launched in 2022 to deliver fast and flexible on-demand infrastructure while helping organizations meet security, identity, and compliance requirements.
But even with Security Hub and other AWS tools, companies are still unprotected from threats and data breaches. In 2022 alone, there were more than 4100 publicly disclosed data breaches, some of which interfered with well-known companies such as Meta, Samsung, and Twitter.
Many factors contribute to your cloud security. This article discusses some limitations of AWS cloud security and offers practical steps to improve it.
Who is responsible for Cloud security in AWS?
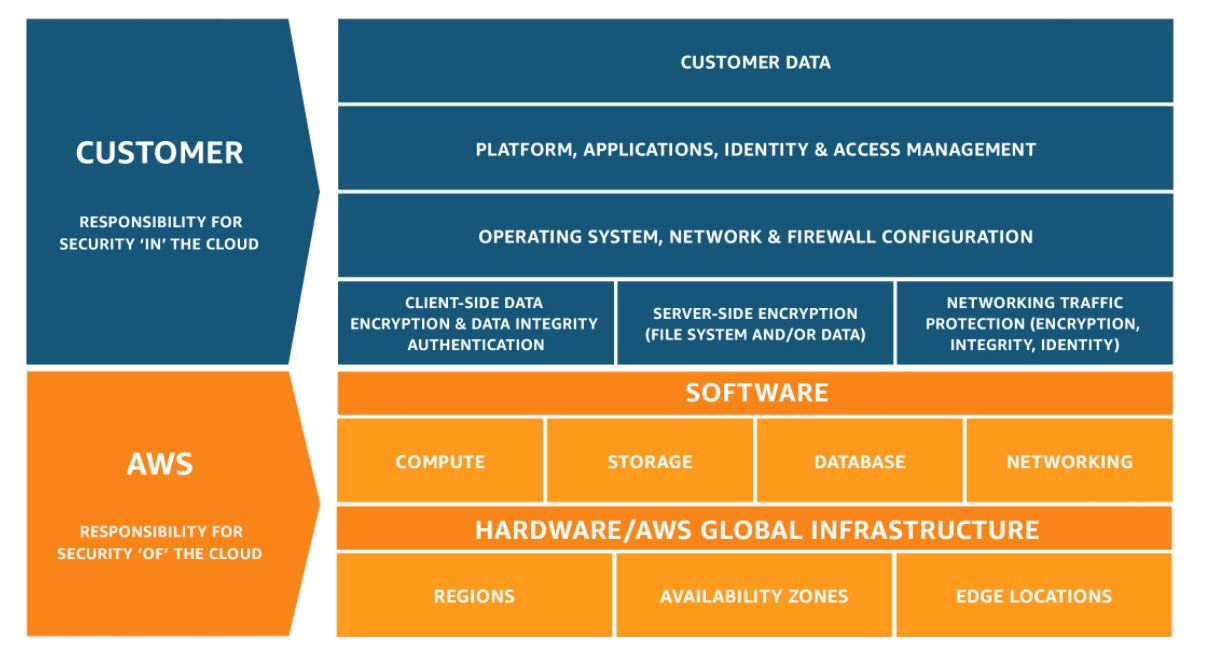
AWS operates on the security model of shared responsibility. In other words, AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud, such as its data centers and network architecture. Its customers are responsible for security in the cloud, such as operating systems and applications.
Customer responsibilities can expand or decrease depending on the AWS service chosen. Installation of third-party tools may be necessary to take ownership and strengthen security measures.
As the most widely-used cloud solution in the marketplace today, AWS has 96 Availability Zones in 30 geographic regions worldwide. AWS offers over 200 products and services that range from cloud computing to storage, migration, databases, messaging, analytics, management tools, and networking and security.
Here are a few of its most widely used services:
- Elastic Search – a free open search and analytics tool for data
- Amazon EC2 – a virtual server that scales computing in the cloud and deploys applications faster
- RedShift – an analytics database that can store and query large volumes of data
- Amazon Lambda- a serverless computing platform that runs code without the need to manage servers to scale automatically
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk – a service that deploys and scales web applications and services
10 essential steps to improve your AWS cloud security today
Customer responsibility for security varies according to the AWS services they use and their integration into the IT environment. But the flexibility and control that AWS offers rely on the shared responsibility model (SRM) to meet security and compliance. The actions customers take within their organizations are essential.
Let’s look at some steps you can take now to improve your AWS cloud security.
1. Improve visibility into your cloud
Although many cloud administrators grant permissions to all employees, most users only use 8-10 of these permissions. Malicious threat actors sometimes use the remaining ones to access your data and network. Skyhawk monitors your entire infrastructure, including used and unused permissions, to deliver comprehensive visibility to your cloud across many domains.
For organizations with services on different public clouds, complete visibility is crucial. Cross-cloud visibility also ensures you know exactly when and how your attack surface changes and improves your ability to detect unusual behavior. In addition to security benefits, cross-cloud visibility results in maximum uptime and quality of experience (QoE) and improved forecasting, planning, and management of the state of future cloud applications.
2. Develop an internal framework
Frameworks give organizations from different countries and industries a clear set of standards to ensure minimal risk. In addition to the relevant industry frameworks such as NIST, SOC, and GDPR, you should develop an internal framework within your organization.
Employees must understand the security step they should take — from identity to protection, detection and incident response, and recovery — to guard against and mitigate cybersecurity threats. Adopting the right tools can help your organization boost protection at every step.
3. Use strong authentication
The days of allowing access to the cloud through a username and password are gone. Instead, the identity of users ensures security and compliance. Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions help organizations maintain and control access to these user identities. IAM solutions do this through several different features like multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to sign in through several different types of identification, such as a username, password, and a one-time password.
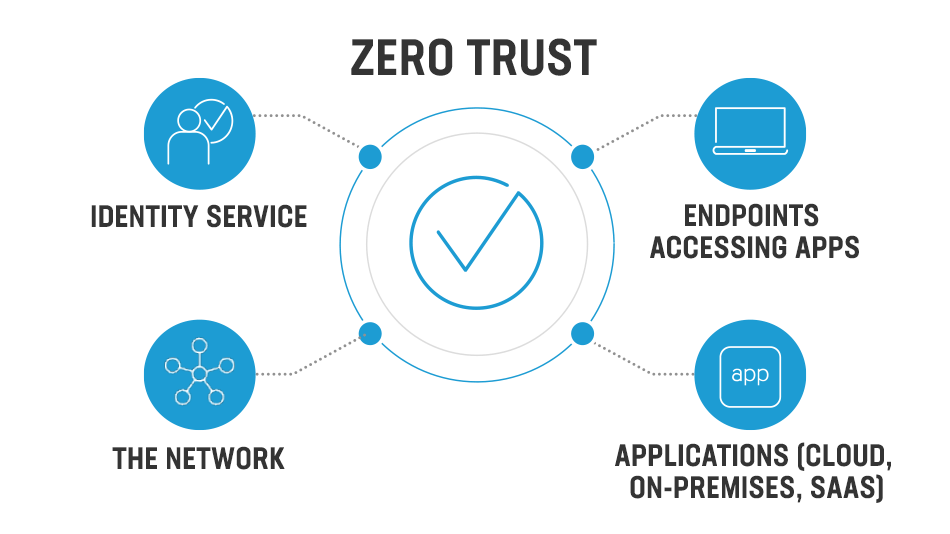
4. Implement a zero trust policy
No employee should have administrative access to the cloud or be able to change configurations. Zero trust policies replace the implicit trust of employees inside the security perimeter with explicit trust (e.g., granting permissions based on employee roles). These granular permissions should be evaluated and monitored on an ongoing basis to ensure that no employee has more access to cloud services than required for their role.
5. Protect sensitive data
Malicious threat actors constantly try to access sensitive data and malware. Organizations must conduct ongoing scans to identify any data or malware that could be open and accessible. Skyhawk’s runtime hub goes further by correlating activities from any log or source for live detection and response. Organizations can take a more proactive approach to prevent hacking, data breaches, and the installation of malware by setting up a trusted execution environment (TEE).
6. Continuously log your cloud environment
Turning on logs in your environment provides a few security benefits. First, security teams can monitor them in real-time and proactively guard against attempts by malicious actors to infiltrate your network. In addition, logs provide details of the attacker after an incident, such as the date and time of the incident, their IP address or source, the resources they attempted to access, and whether or not they were successful. Finally, logs also help identify the source of connectivity issues and resolve them more quickly.
7. Train employees on AWS best practices
Since AWS cloud relies on shared responsibility, it has extensive documentation and training on securing the AWS Cloud. These include exercises to help determine the compliance requirements and industry frameworks like NIST and ISO your organization needs to consider. Online training programs such as the Cloud Audit Academy offer training to teams to learn the skills and stay updated on best practices.
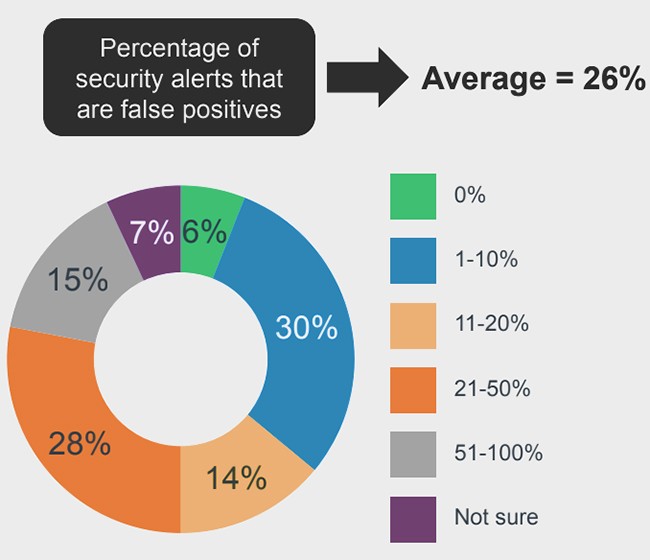
8. Avoid false positive alerts
Organizations always want to ensure they get all the security alerts, so they typically have a low threshold for what constitutes an alert. But since their solutions don’t understand these threats in context, these alerts are often one-off behaviors rather than “real” alerts.
In contrast, Skyhawk uses rule-based and machine-learning-based detectors not only to identify relevant potential threats but to continually view them in their proper context so that they are on your radar when they become relevant. For example, instead of alerting your organization to any excessive permissions or a compromised server, it would alert you to users logging in from an unidentified location at a strange time.
9. Automate your detection process
With enterprise-level organizations using more than 150 applications and an average of 2.6 public cloud services, detecting security threats is becoming increasingly complex. Advanced automated detection tools can help streamline the process of securing your entire cloud and assets across many domains, including how users and applications access specific hosts, users, networks, and firewall functions. When an attack does happen, it can also respond more quickly.
10. Monitor compliance
While AWS delivers visibility into your compliance status with automated compliance checks based on the shared responsibility model, Skyhawk offers free compliance verification. Our multi-layered approach covers the overall security posture of the cloud to prevent compliance violations, and provides step-by-step instructions to resolve any violations that arise. These compliance needs have only increased due to the global shift in remote work across geographic locations globally.
Bolster your security posture in AWS
Considering that 60% of the world’s business data is on the cloud and that digital transformation will accelerate that process, it’s no surprise that cloud security is a top priority for security leaders today. As the cloud provider with the largest market share today, AWS provides many cloud security tools to its customers — but only up to a point. By taking the steps outlined in this post, organizations can defend their cloud and assets and optimize their security of the cloud and in the cloud. With Skyhawk, Cloud Security Posture Management is entirely free. Learn more.