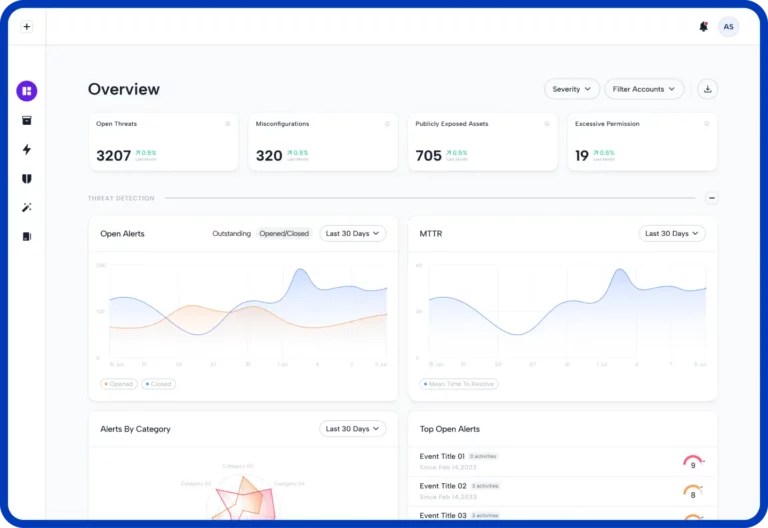
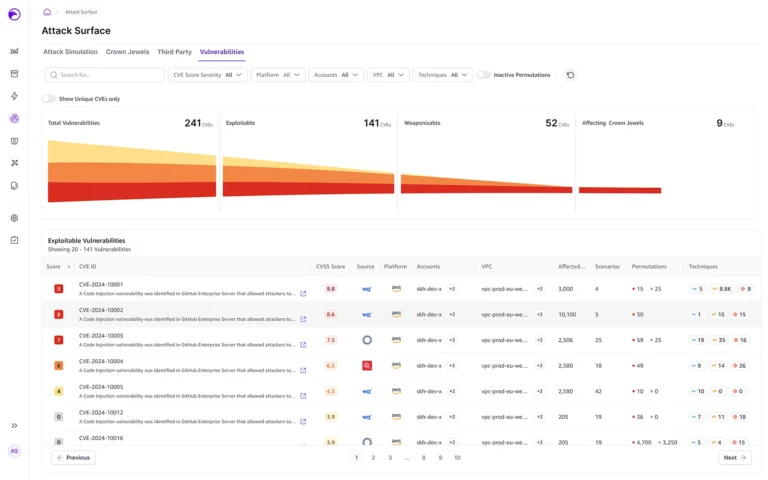
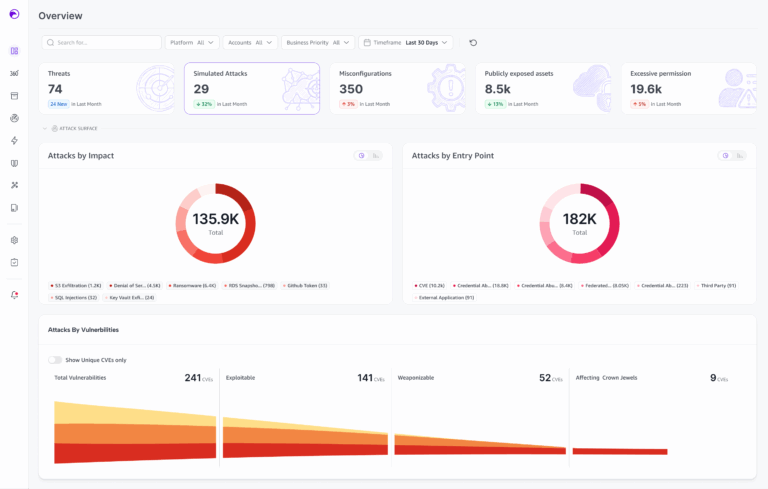
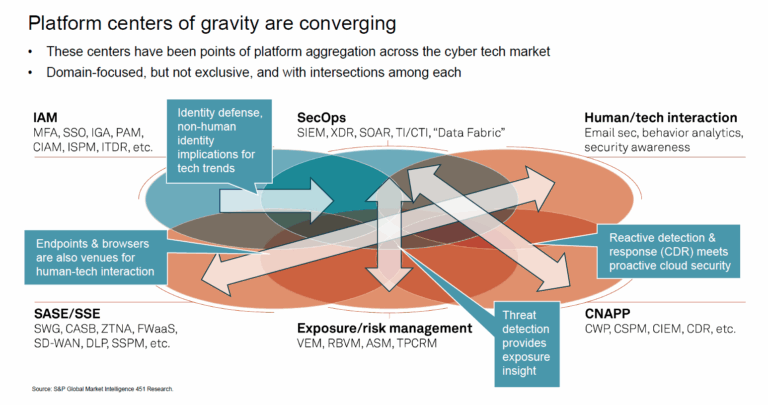
When evaluating a cloud security solution, it is imperative to know how well it will detect threats in time to prevent a breach.
Here are three examples out of many in which our customers were able to detect an incident and stop it in time to prevent a full-blown breach.
Incident 1: Trying to take Advantage of New Year’s Eve
Overview of the incident: This incident occurred over a holiday when everyone was off guard. Skyhawk’s platform identified and alerted on the incident within 3 minutes of activity.
Initial Access Method: The attack’s initial access method leveraged leaked keys mistakenly left on a CI server. CI servers are used to build and deploy software changes as part of the CI/CD pipeline and therefore tend to have excessive permissions for a reason.
Lateral Movement: Once in, the attacker attempted privilege escalation a technique in which entity permissions are modified to higher privileges. This action triggered an alert. At this point, the customer already had the ability to implement automated response, reverting the permission escalation and disabling the entity, both operations would have stopped the attacker without any impact on production systems. In our case the customer decided to wait with the response and collect more evidence. The attacker’s next steps were slowly progressing, identifying additional resources and users for persistence as well as attempting to block the customer from responding to the attack and hide his goals. One of the attacker’s persistency actions was to create a new access key, at this point it was enough for the SOC and IR team to intervene and remove the key, delete cloud assets, revert the permissions escalated and start a hardening process including key rotation.
Incident 2: Attempting to exfiltrating data
Overview of the incident, key takeaway: Once an attacker is in, they can access the cloud vendor’s security solution to evade detection, therefore as a customer you must use multi layered security using 3rd party tools.
Initial Access Method: The attackers obtained a user’s credentials and used them to access the customer’s cloud.
Lateral Movement: With the leaked user’s credentials the attacker then created a parallel infrastructure and was able gain access to database.
In parallel to the lateral movement activity, the attacker did something very interesting, they executed API calls to the cloud-native security tools to see if they had been detected by it.
It is important for organizations to know, when your cloud is compromised, you should take into account that all cloud services are compromised, including cloud-native security services. This invaluable insight enables threat actors to understand how to outmaneuver cloud-native security services to stay undetected as well as lay the groundwork for future attacks. Skyhawk is an out-of-band security solution, so it was not possible for the attackers to access it and check if they were detected which indicates how critical it is to use a 3rd party solution to protect your cloud on top of the native services.
These abnormal and risky activities were enough for the Skyhawk platform to issue an alert.
Attempted Impact: The attacker’s attempted impact was data exfiltration from a database. They tried to move slowly, to ensure they were not detected and were attempting to exfiltrate the data at low volumes, again, to avoid detection. However, before they could do that – Skyhawk raised an alert and prevented the exfiltration from ever happening.
Incident 3: Insiders cannot outrun Skyhawk Security
Overview of the incident, key take away: A rogue employee, with knowledge of the systems, the detection mechanism and no need to make any lateral movement is very hard to detect. Yet Skyhawk’s advanced detection algorithms were used as another line of defense were able to detect the rogue employee.
Initial Access Method: Legitimate login leveraged by an employee doing illegitimate activity similar to a malicious insider and an employee (doing illegitimate activity).
Lateral Movement: None required, this was a legitimate insider
Attempted Impact: At a major global firm, an insider tried to leverage corporate resources for malicious activities for personal financial incentive. The insider had hands-on access to Kubernetes cluster, so no lateral movement or privilege escalation was required.
In contrary to an outside attacker with limited access, he had all the time in the world, also making it hard to distinguish his illegitimate activity as a legitimate user. Still the employee moved low and slow.
For example, since the employee felt he has all the time he needs, the clusters he created were not large so as not to draw much attention. But this employee made one critical mistake trying to access networks that aren’t part of the organization’s usual network traffic for which the Skyhawk platform triggered an alert. The employee was caught within minutes of the unusual network activity before he was able to create a major financial impact on the company. His account was terminated and as you can imagine, he was escorted out of the building by security. Even an experienced insider was not able to outsmart the multi layered defense of the Skyhawk’s platform.
Conclusion
When evaluating cloud security solutions, it is important to examine real use cases and understand how such solutions will address these. Skyhawk’s technology has proven itself capable of promptly detecting very complex and advanced incidents. Try the Skyhawk platform for free for 30 days – click here to subscribe!