As cloud adoption continues to gain traction, so do the risks and challenges of its security. The latest Google Cloud Threat Horizons Report for the first half of 2025, titled:” Evolving Ransomware and Data Theft Risks in the Cloud”, highlights critical emerging threats that organizations must address to protect their cloud environments. The report highlights several vectors that pose significant risks to cloud security, including: service account exploitation, identity-based attacks, cloud database vulnerabilities, and diversified attack strategies.
Service Account Exploitation
Service accounts, often used for automation and application integration, have become a prime target for cybercriminals. Attackers are increasingly exploiting over-privileged service accounts, leveraging their permissions to move laterally within cloud infrastructures. When compromised, these accounts provide an entry point for attackers to gain deeper access, execute malicious code, and exfiltrate sensitive data. To mitigate these risks, organizations must enforce the principle of least privilege (PoLP), regularly audit service account permissions, and implement continuous monitoring solutions to detect unauthorized activity.
Identity-Based Attacks
With identity being the new perimeter in cloud security, attackers are focusing on credential theft, session hijacking, and social engineering tactics to gain unauthorized access. The Google report highlights a rise in identity-based attacks, particularly in hybrid environments where cloud and on-premises identities overlap. Threat actors use phishing campaigns and credential stuffing attacks to exploit weak authentication mechanisms. To combat these threats, businesses should deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA), adopt zero-trust security models, and implement identity threat detection tools to spot anomalies in user behavior.
Cloud Database Vulnerabilities
Cloud databases are the organization’s “Crown jewels”,treasure troves of sensitive information, making them attractive targets for attackers. The report reveals that misconfigurations, weak credentials, and lack of proper access controls are among the leading causes of cloud database breaches. Threat actors exploit these weaknesses to access and exfiltrate valuable data. To strengthen database security, organizations must enforce strict access controls, regularly update and patch database management systems, and utilize encryption to protect data at rest and in transit.
Diversified Attack Strategies
Cybercriminals are evolving their tactics to maximize profits from compromised cloud accounts. One emerging trend is privilege escalation attacks, where attackers gain higher-level access to execute malicious operations. Some threat actors have also been found exploiting cloud billing accounts, charging victims for unauthorized services and creating financial strain. To defend against such threats, organizations should implement continuous monitoring, use anomaly detection systems, and limit the creation of high-privilege accounts.
Strengthening Cloud Security
As cloud threats continue to evolve, organizations must proactively strengthen their cloud security posture. The trends detailed at the Google report illustrate the sophistication and velocity in which attacker move to attack cloud environments. In order to counter these, organizations must employ the most advanced security technologies.
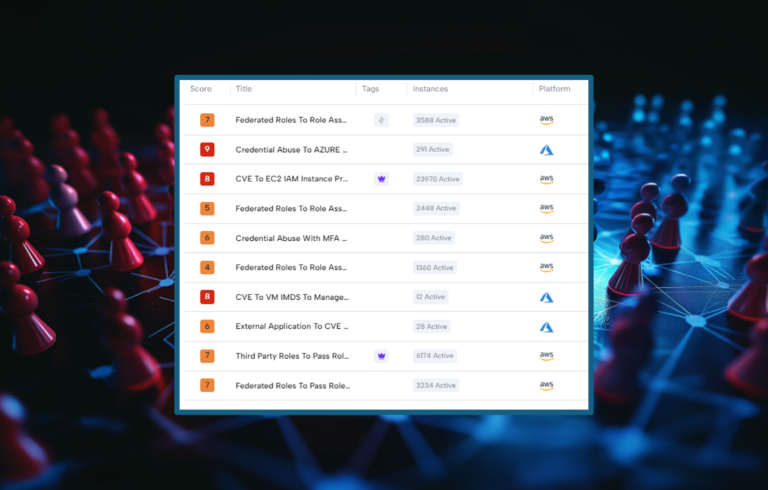
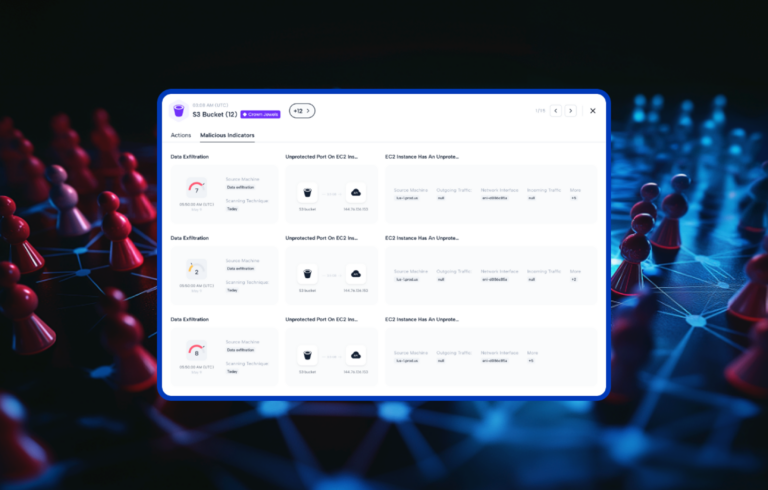
Skyhawk Security’s Continuous Proactive Protection helps organizations discover their crown jewel assets and then the GenAI-based red team and blue team see how defenses hold up against an attack. Skyhawk Interactive CDR adds another layer of control, an out of band verification by the cloud asset owner. It further improves cloud security operations with immediate verification of the alert.
Try Skyhawk Security for free today!